AI Implications
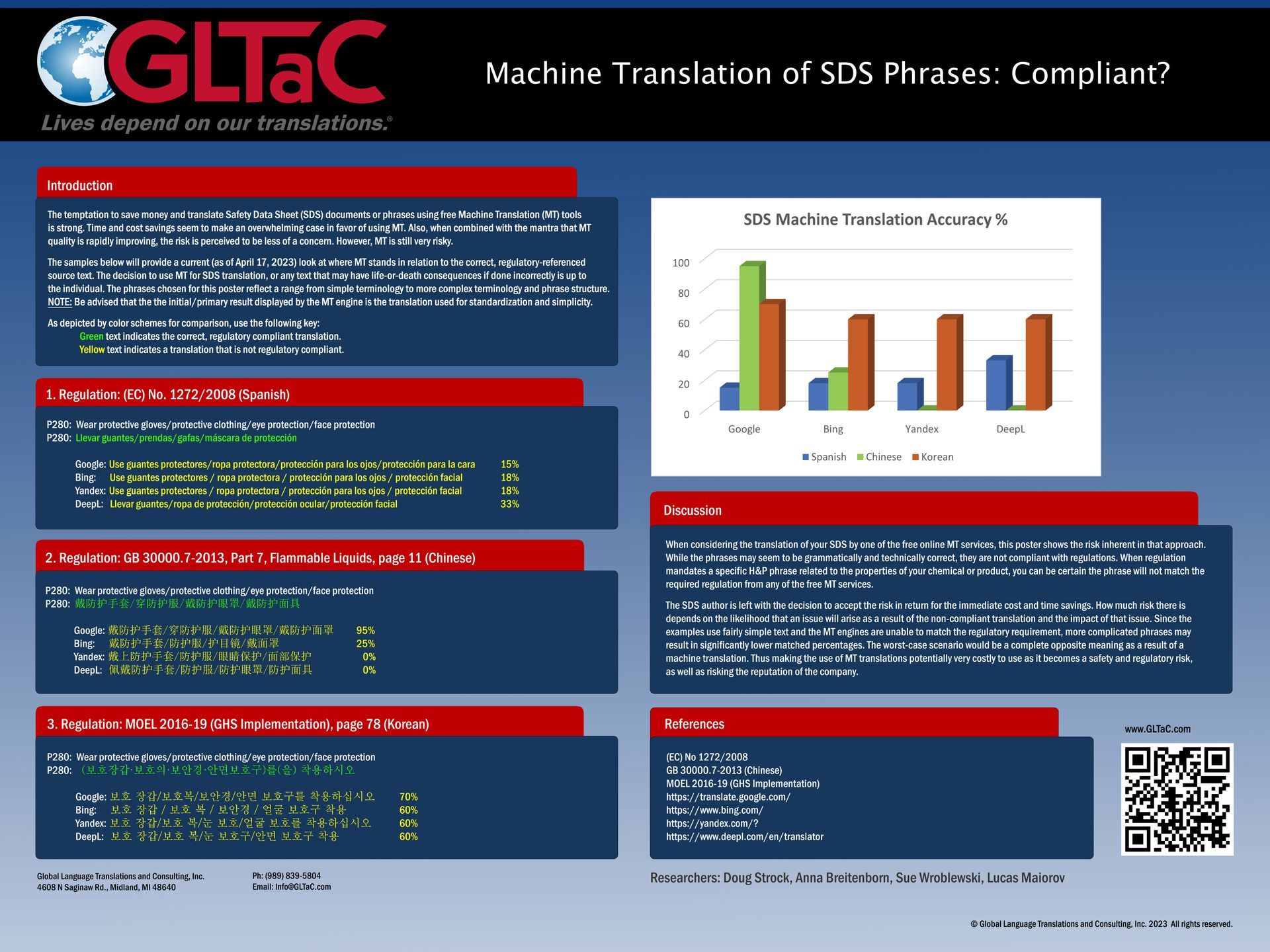
Human Insight, Legal Foresight: Translations You Can Trust
ABA Legal Guidelines: Legal Considerations when using AI for Language Translations

The adoption of Resolution 604 by the American Bar Association's House of Delegates in 2023 could have several significant implications for the language translation business, especially those using or considering the use of AI in their services. Here's how it might impact the industry:
- Increased scrutiny on AI use: Language translation companies using AI-powered tools may need to be more transparent about how they implement these technologies in their workflows.
- Accountability measures: Businesses may need to establish clearer accountability structures for decisions made using AI in translation processes.
- Traceability requirements: There might be a need to implement systems that can trace AI-assisted translations back to their source, showing how decisions were made.
- Quality assurance: Companies may need to develop more robust quality assurance processes to ensure AI-translated content meets the same standards as human translations.
- Privacy and data protection: As AI systems often require large datasets for training, there may be increased focus on how translation companies handle and protect client data.
- Ethical considerations: The resolution may prompt discussions about the ethical use of AI in translation, particularly in sensitive fields like legal or medical translation.
- Human oversight: There may be a greater emphasis on human oversight of AI-assisted translations, especially for critical documents.
- Disclosure to clients: Translation companies might need to be more upfront with clients about when and how AI is used in their translation processes.
- Regulatory compliance: As regulators begin to implement guidelines based on this resolution, translation companies may need to adjust their practices to remain compliant.
- Competitive advantage: Companies that can demonstrate adherence to these guidelines may gain a competitive edge, especially when working with legal clients or in highly regulated industries.
- Investment in technology: To meet these new standards, companies may need to invest in more sophisticated AI systems that offer better transparency and traceability.
- Training and education: There may be a need for increased training for translators and project managers on the ethical use of AI and how to work alongside AI systems responsibly.
While the resolution itself is not legally binding, it sets a standard that could influence future regulations and client expectations in the language services industry. Translation companies, especially those serving legal clients or working in regulated industries, should consider how to align their AI practices with these guidelines to stay ahead of potential regulatory changes and meet evolving client needs.

Human Translation: Advantages
Advantages of Human Translation:
- Contextual understanding: Humans can grasp nuances, idioms, and cultural context that AI might miss.
- Creativity: Humans can creatively solve translation problems, especially with marketing or literary texts.
- Ethical decision-making: Humans can make ethical judgments about sensitive content.
- Accountability: There's a clear line of responsibility with human translators.
- Confidentiality: Humans can better ensure client confidentiality without data being stored in AI systems.
- Specialization: Human translators can specialize in specific fields, bringing subject matter expertise.
- Quality assurance: Humans can perform thorough quality checks, understanding the intent behind the text.
- Adaptation: Humans can quickly adapt to new guidelines or client preferences.
- Complex document handling: Humans excel at managing complex document formats and layouts.
- Client communication: Human translators can directly interact with clients for clarifications.

Using AI for Translation: Legal Implications
Potential Legal Implications of Using AI for Translations:
- Accuracy liability: Errors in AI translations could lead to legal issues, especially in fields like chemical, medical or legal translation.
- Intellectual property concerns: AI systems trained on copyrighted materials could raise IP infringement issues.
- Data privacy: Use of client data to train AI systems could violate privacy laws like GDPR.
- Confidentiality breaches: AI systems might not adequately protect sensitive information, leading to potential legal action.
- Lack of certifiability: In legal contexts, AI translations might not be accepted as certified translations.
- Regulatory compliance: AI systems might not keep up with rapidly changing regulatory requirements in certain industries.
- Transparency issues: Lack of transparency in AI decision-making could be problematic in legal disputes.
- Bias and discrimination: AI systems might perpetuate biases, leading to potential discrimination claims.
- Contract fulfillment: Use of AI without client knowledge could be seen as a breach of contract in some cases.
- Professional liability: Reliance on AI without proper oversight could be seen as professional negligence.
- Cross-border legal issues: AI systems might not account for different legal systems and terminologies across jurisdictions.
- Authorship and copyright: Questions may arise about who owns the copyright for AI-generated translations.
- Duty of care: There could be questions about whether using AI meets the required standard of care in professional services.
- Informed consent: Failure to disclose AI use to clients could lead to legal issues around informed consent.
- Auditability:
Lack of clear audit trails in AI systems could be problematic in legal proceedings.
In Conclusion:
These factors underscore why many businesses, especially those dealing with sensitive, high-stakes, or legally significant translations, often prefer human translation services. While AI can be a powerful tool, its use in translation requires careful consideration of these legal and practical implications. Companies using AI in translation should implement robust oversight, quality control, and disclosure practices to mitigate potential legal risks.